GEOB 307–Discrepancies Among the Range Maps for Rubus armeniacus and Sturnus vulgaris
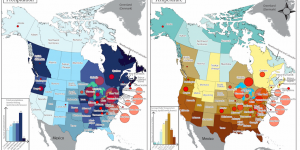
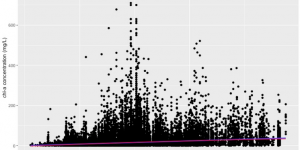
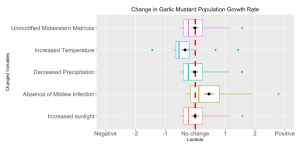
The species range map is the assessment of species distribution and dispersal patterns in a particular location. This map will provide information that helps to connect the geographical displacement with ecological, climate, and environmental factors. The species range map uses metadata, experimental results, ecological modeling, and taxonomic experts’ prediction to create a visual explanation of why species are found in particular habitats.